Cellulose-Based Adsorbents for Decontamination of Multi-Pollutant Contaminated Waters
Porous spherical adsorbents based on natural biopolymers, pure and co-doped with activated carbon (AC), were prepared via dropping cum non-solvent-induced phase separation from ionic liquid–based solution.
Dr. Alexandra S. M. Wittmar, Lehrstuhl für Technische Chemie II, Universität Duisburg-Essen
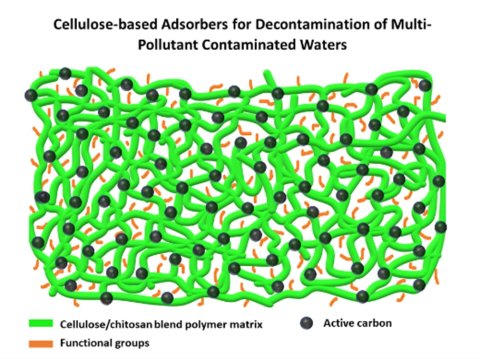
Their adsorption properties toward different types of model pollutants were evaluated. Blending of cellulose with chitosan (cellulose/chitosan = 75/25 wt/wt) led to improved adsorption of Cu2+ and methyl orange (MO). Co-doping with AC (10 wt % with respect to the biopolymer) clearly improved adsorption of dyes and tetracycline (TC) but slightly reduced adsorption of Cu2+. From mixed pollutant solutions, it was observed that TC and methylene blue can be adsorbed without competing for the same adsorption sites, whereas Cu2+ and MO slightly compete.
Dr. Alexandra S. M. Wittmar, Lehrstuhl für Technische Chemie II, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Universitätsstr. 7, 45141 Essen, Germany
[email protected]
DOI: 10.1002/cite.70020